Chest CT Findings in Patients with COVID-19
Allan S. Brett, MD reviewing
This report provides a detailed account of initial computed tomographic abnormalities in 51 hospitalized patients.
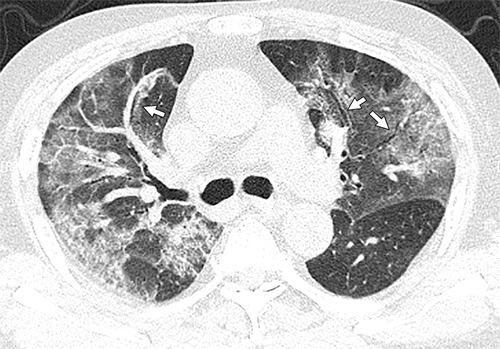
Figure 2d:(a, b) Baseline CT images at admission of a 75-year-old man show multiple patchy areas of pure ground-glass opacity (GGO) and GGO with reticular and/or interlobular septal thickening. (c, d) Follow-up CT images on day 3 after admission show overlap of organizing pneumonia with diffuse alveolar damage in that it is more diffuse (not rounded) and associated with underlying reticulation, prominent progression with increased size and density of the lesions, and with more consolidations. Air bronchogram is also shown in d (arrows). Interlobular septal thickening does not seem to be major component. There is reticulation in many of cases of both suspected organizing pneumonia and diffuse alveolar damage.
Chest computed tomography (CT) will be performed in most hospitalized patients with COVID-19. In this report from a single hospital in Shanghai, China, researchers reviewed the key initial CT findings in 51 consecutive patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19. All patients had thin-section noncontrast scans. Mean age was 49 (range, 16–79), and median time from symptom onset to CT was 4 days.
Nearly all patients presented with extensive multifocal involvement; abnormalities were bilateral in 86% of cases. Lesions were particularly evident in the lower lobes, posterior lung fields, and peripheral lung zones. Three quarters of patients had ≥3 involved lobes. Various combinations of pure ground-glass opacities (GGOs), GGOs plus reticular or interlobular septal thickening, and GGOs plus consolidation were common. GGOs predominated in patients whose symptoms started ≤4 days before CT, and areas of consolidation became increasingly evident in those with >4 days of symptoms. Only four patients had pleural effusions.
Song F et al. Emerging 2019 novel coronavirus (2019-nCoV) pneumonia. Radiology 2020 Apr; 295:210. (https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020200274)